How to fly an NDB: Difference between revisions
(→ADF) |
(→homing) |
||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
Station passage is indicated by the needle sweeping from pointing forward to pointing aft, and the closeness of passage is indicated by the speed of the needle transition. A good station passage occurs relatively quickly, whereas a poor passage passing abeam has the needle move more slowly as it points to the antenna passing to one side of the aircraft as the aircraft flies by. | Station passage is indicated by the needle sweeping from pointing forward to pointing aft, and the closeness of passage is indicated by the speed of the needle transition. A good station passage occurs relatively quickly, whereas a poor passage passing abeam has the needle move more slowly as it points to the antenna passing to one side of the aircraft as the aircraft flies by. | ||
=tracking= | |||
A track-made good may be established by turning the aircraft into wind to counter the wind-drift such that the NDB needle relative bearing will remain constant and the aircraft will track to or from the NDB on the one bearing or radial. | |||
==departure== | |||
Should the aircraft depart with the desired heading set then the ADF needle will show a constant reading with the needle indicating the angle of drift. | |||
[[image:ndb-departure-constant-heading.png]] | |||
=references= | =references= | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 21:21, 22 February 2023
Introduction
It is advantagous to understand how both an Non Directional Beacon and Automatic Direction Equipment work when appreciating how to fly using an NDB and ADF.
NDB
An Non Directional Beacon is comprised of an omni-directional Vertically polarised (usually capacitively top-loaded) antenna at a known stationary location coupled to a Medium to Low Frequency Transmitter that has an amplitude modulated identification of one, two or three-letter Morse Code callsign. In Australia they use the three-letter Airport Code when located at an airport.
The NDB is described in ICAO Annex 10 that specifies that NDBs operate between 190 kHz and 1750 Khz, as a consequence an ADF may receive AM broadcast stations when you place the ADF into receive only mode, or a known broadcast station may be used for homing and fixing and for these purposes some AM broadcast frequencies are listed in the ERSA.
There are a few types of NBs:
- En route used to mark airways for homing etc
- Approach NDBs that have a hold and approach associated with them
- Localiser beacons for guidance to an ILS
- Locator beacon for guidance to an ILD
- some AM broadcast stations that may consequently be used in navigation
ADF
The Automatic Direction Finding equipment is a form of Radio Compass that provides the pilot with a relative bearing of the NDB. The needle will point to the beacon with the aircraft nose being straight ahead.
A radio wave consists of two electromagnetic components; an electric field (E-field) and a magnetic field (H-field) that are orthogonal to each other in space, and their amplitudes vary sinusoidally with time. The E-field of an NDB antenna is vertically oriented perpendicular to the ground, and the H-field is oriented horizontally parallel to the ground.
The ADF system contains a loop antenna where the H-field induces signals, and a sense antenna that has signals induced by the E-field (The sense antenna is either wire or a short antenna in the same housing as the loop antenna e.g. in a KR-87 antenna housing).
The KR87 loop antenna consists of two mutually perpendicular coils on a square ferrite core. The axis of one winding is aligned along the longitudinal axis of the aircraft and the voltage induced in the coil is the sine of the angle between the nose of the aircraft and the beacon antenna. The other coil winding is aligned laterally to the aircraft (i.e. parallel to the wings) and the voltage induced in it is the cosine of the relative bearing between the nose of the aircraft and the beacon.
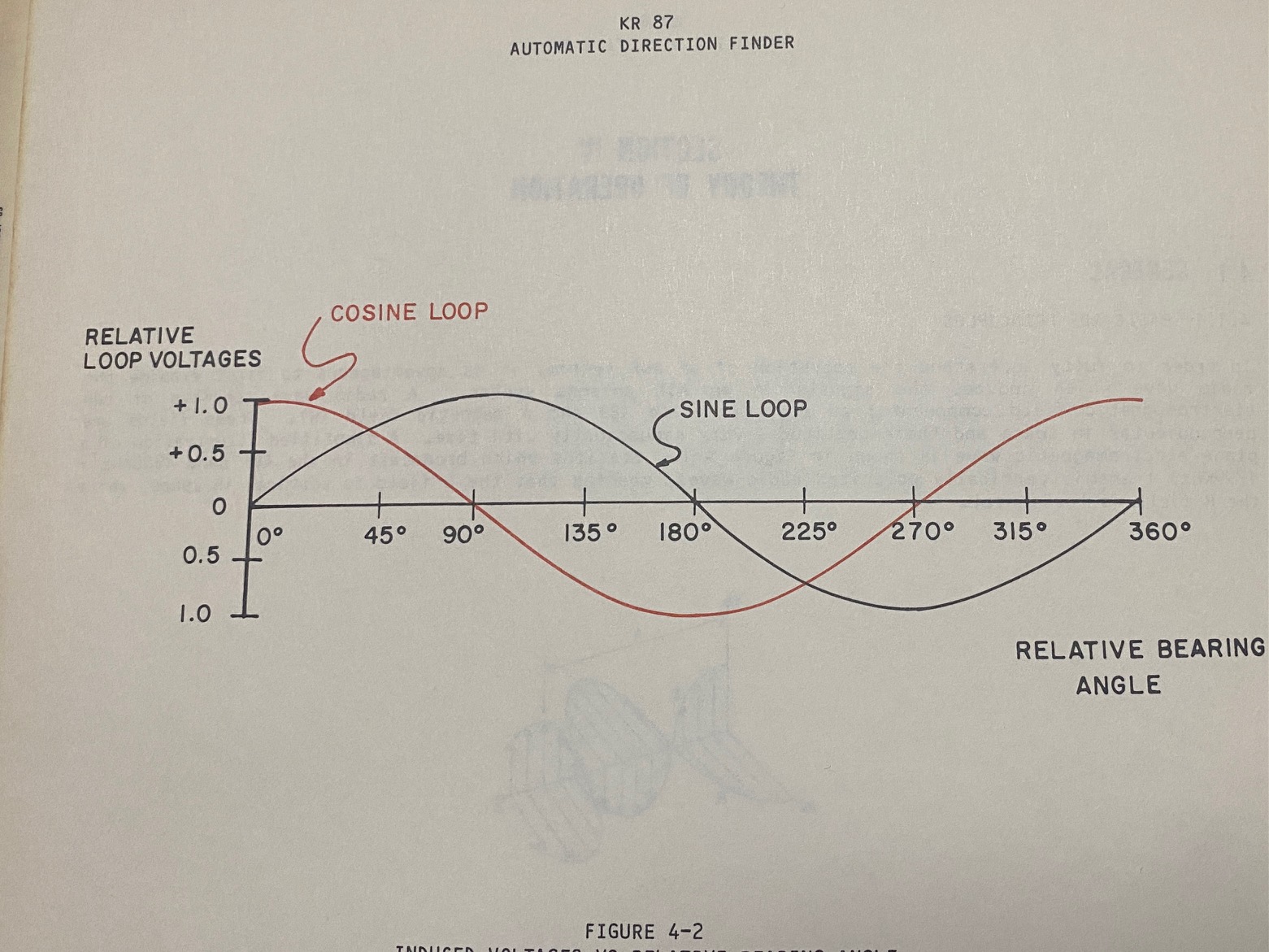
The KR87 uses a sense antenna with phase correction to provide disambiguation of the correlation of equal sine and cosine curves at 45 degrees and 225 degrees relative bearing. These sine and cosine signals are demodulated via a balanced demodulator (switched at 32 Hz - the hum you can hear) and summed with the sense antenna signal that is in phase quadrature with the demodulated loop antenna signals. This summation of three signals results in a quadrature signal that provides the relative angle to the station.
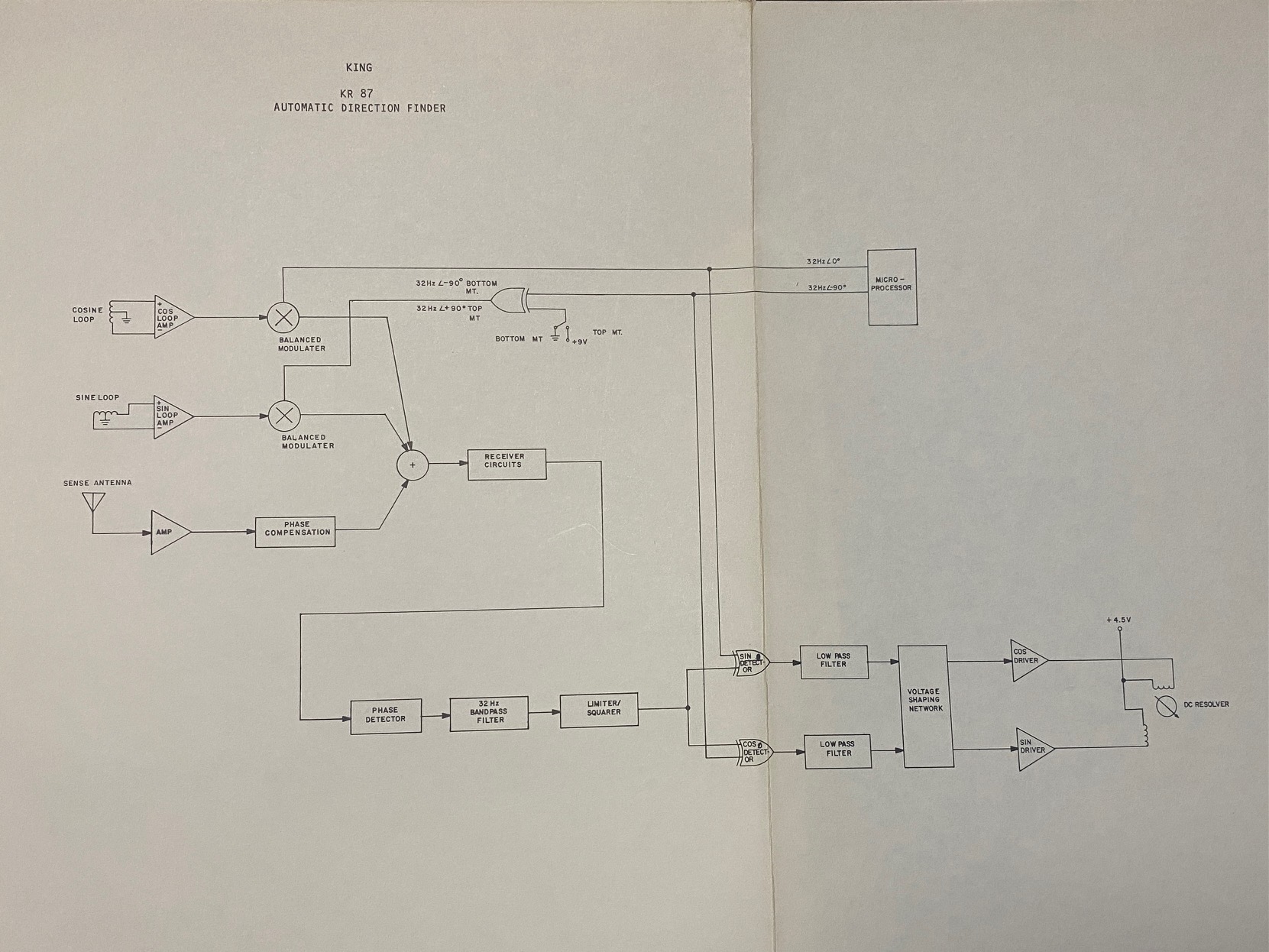
The signals are integrated to produce two D.C. analogue voltages to drive the indicator needle in the resolver. The needle of the resolver indicator thus will provide a bearing relative to the aircraft nose.
Since the laterally oriented coil is along the axis of the wings, its response is subjected to errors caused by the angle of bank. This is common referred to as quadrantal error, however, in the KR87 manual it lists any error in quadrant sense as quadrantal error and may actually be caused by aircraft antenna installation and structure. They have adjustments that may be used to correct the "out-of-round" errors - however they cannot adjust out errors caused by bank angles as there are no gyroscopic inputs into the KR87 ADF, nor most others that I am aware of.
Australian and USA Automatic Direction Finding equipment are TSO-C41d with 1kHz steps (which is slightly different to DO-179 that provides for 0.5kHz tuning resolution in Europe)[1]
http://www.airwaysmuseum.com/NDB%20BLT%202-05.htm#
limitations
propagation
The NDB radio waves have two paths:
- along the ground - which may go beyond the line of site - termed ground-wave
- and ducting and reflection between the ground and the ionosphere - termed sky-wave or colloquially skip.
During the day the D-layer of the ionosophere attenuates the lower frequencies so it is unusual for sky-wave propagation to occur with NBD and Broadcast stations, but at night this layer is not present and signal can propagate over very long distances via ionspheric and ground reflections depending on the distance from the station and the details of the ionosphere. The mixing of ground-wave and sky-wave introduces amplitude, polarisation and phase variations that may affect the workings of an ADF receiver. This may result in erroneous readings.
The night time range of moderately powered NDB beacons is 60 miles over land and 100 miles over the ocean and beyond these ranges they will be subjected to propagation effects, particularly at night.
Low power beacons that only have a range of 30 miles or so are largely unaffected by ionospheric propagation.
Lightning
Lighting strikes can be both vertically and horizontal polarised depending on whether they are ground or inter-cloud strikes respectively, and are often produce broad frequency radio waves of such magnitude that they will temporarily cause the ADF needle to deflect from the relative bearing.
People say the needle will point to the storm, thus the accuracy of the ADF needle will vary when flyng near a storm.
co-channel interference
If a NDB is operating on the same of an adjacent frequency to another NDB then there are likely to be resolution errors in the relative bearing; these errors cannot be corrected or allowed for and it is important to understand what co-channel interference sounds like and its effects. The errors may be serious is the ADF is tuned to an NDB beyond it usable range. You must always check the integrity of the identification, the signal and the indicated relative bearing by some other means. (You could also tune to a strong broadcast station to roughly verify your position.)
mountain effects
If you are flying in or across mountainous terrain the ground reflections from the slopes of the hills can affect the polarisation and phase of the NDB signal. These other reflected signal mix with the ground-wave signal and introduce errors that vary of terrain and hence time. Bearings will be found to vary rapidly until the affected area is passed.
range
The range of an NDB is affected by the power of the transmitter and antenna system, and the terrain over which the ground-wave propagates, Lossy ground reduces the ground-wave propagation, where as highly conductive ground, such as swampy soil, or the ocean significantly increased the range of reception of an NDB.
The signal from and NDB also increases over unfavourable (poorly conductive soil) with aircraft height above ground.
back bearing
It is better to use the back bearing to an NDB that you have overly flown, and only tune to a forward facing NDB when about half-way on track as the back bearing will be superior.
homing
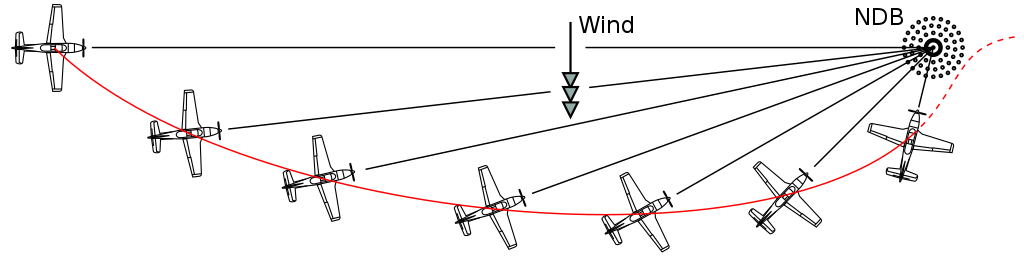
Homing is the procedure of placing the NDB relative bearing needle on the nose of the aircraft by changing the aircraft heading to keep the needle head on the nose of the aircraft.
When there are crosswinds homing will result in a curved path, but it will always result in the aircraft flying towards the station with station passage almost guaranteed.
Station passage is indicated by the needle sweeping from pointing forward to pointing aft, and the closeness of passage is indicated by the speed of the needle transition. A good station passage occurs relatively quickly, whereas a poor passage passing abeam has the needle move more slowly as it points to the antenna passing to one side of the aircraft as the aircraft flies by.
tracking
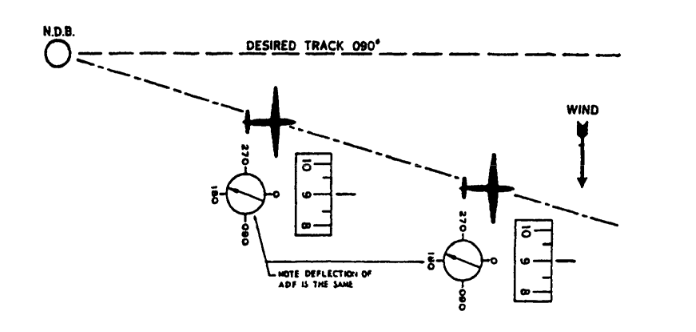
A track-made good may be established by turning the aircraft into wind to counter the wind-drift such that the NDB needle relative bearing will remain constant and the aircraft will track to or from the NDB on the one bearing or radial.
departure
Should the aircraft depart with the desired heading set then the ADF needle will show a constant reading with the needle indicating the angle of drift.